Written by
Sangwan Kwon
on
on
An Overview of GCC
A Compiler
- A computer software that transform transform the source language into the target language.
- Translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language. - The high level programming language: C, C++, Objective-C, Java, Fortran, or Ada - The lower lavel language : assembly language, object code, or machine code
- Each compiler includes three components. a front end, a middle end, and a back end.
GCC (GNU Compiler Collection)
- GCC is not a compiler.
- GCC is a driver program that invokes the appropriate compilation program.
- GCC compiles one file at a time.
- GCC is a compiler collection that consists of three components.
- A front end for each programming language, a middle end, and a back end for each architecture.
- The front end deals with the language itself: scanning, parsing, the parse-tree.
- The back end deals with the target system: object code formats, the machine code itself.
- The gcc (a main GCC executable program) processes source files and produce an assembly file for each source file.
- For a C, ther preprocessor and compiler cc1, the assembler as, and the linker collect2.
Three-stage structure and representations
- A source file goes though all three components one after another.
- The representation is modified when it goes from a component to the next.
- The abstract syntax tree(AST), register transfer language(RTL), and object code are the main representation.
Representations
- The representation is modified when it goes from a component to the next.
- Main representations
- Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)
- GIMPLE
- Register Transfer Language (RTL)
Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)
- Tree representation of the abstract syntactic structure
- All the information the programmer put in his code
- Everything concerning the control flow
- Everything about structures and types
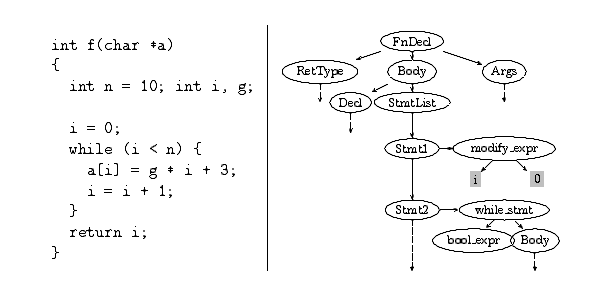
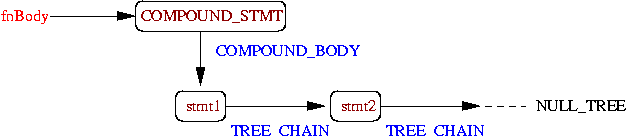
Tree structure on GCC (function)
Function node| Function Body
— | —
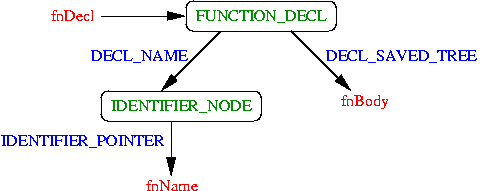 |
| 
#
// Getter by GCC Pluging API
char* fnName = IDENTIFIER_POINTER(DECL_NAME(fnDecl));
tree fnBody = DECL_SAVED_TREE(fnDecl);
Tree structure on GCC (expression)
i = 3 * k + 7;
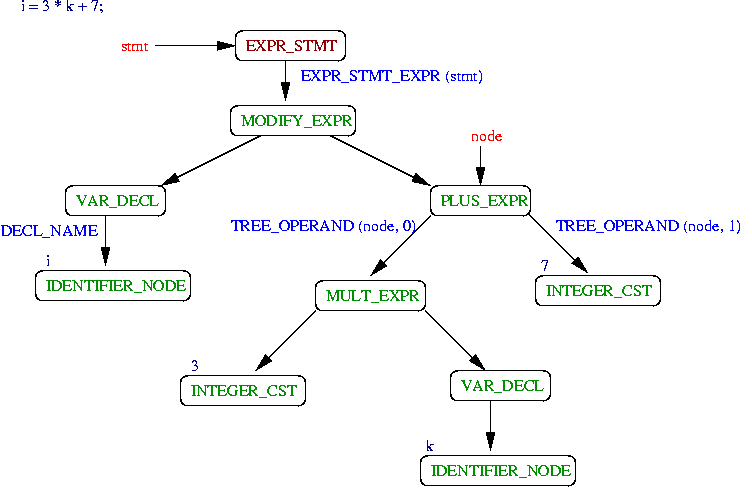
GIMPLE
- Intermediate Representation, IR
- A convenient representations for optimizing the source code
- A subset of the AST/Generic
- Use only the sequencing and branching control flow constructs
- No more than three operands
- Control flow representation
- Conditional statements
- goto operators
- Function calls
Example of GIMPLE
CPP
while (a<=7) {
a = a + 1;
}
GIMPLE
goto <D.1197>;
<D.1196>:;
a = a + 1;
<D.1197>:;
if (a <= 7)
goto <D.1196>;
else
goto <D.1198>;
<D.1198>:;
SSA (Static Single Assignment)
- Also used for optimizations
- Each variable is assigned exactly once
- More than 20 different optimizations on SSA trees
RTL (Register Transfer Language)
- Also used for optimizations
- A kind of intermediate representation (IR)
- Very close to assembly language
- Correspond to an abstract target architecture
- With an infinite number of registers
- looks like a Lisp S-expression
(set (reg:SI 140) (plus:SI (reg:SI 138) (reg:SI 139)))
# It is used to describe data flow at the register-transfer level of an architecture.
Front end
Deal with the programming language itself
- The front end transforms the input program into an intermediate representation (IR) for further processing by the middle end.
- The purpose of the front end is to read the source file, parse it, and convert it into the standard abstract syntax tree (AST) representation.
- The AST is then used to generate a register-transfer language (RTL) tree.
- Because of the differences in languages, the format of the generated ASTs is slightly different for each language.
- The next step after AST generation is the unification step in which the AST tree is converted into a unified form called GENERIC.
- Scan the source file and parse it
- Generate AST
- Convert into a unified form called GENERIC
- The generated ASTs is slightly different for each language
Middle end
Deal with the intermediate language
- After ther front end, the middle end part of the compiler takes control.
- First, the tree is converted into another representation called GIMPLE.
- In this form, each expression contains no more than three operands.
- All control flow constructs are represented as combinations of conditional statements and goto operators, function calls.
- GIMPLE is a convenient representations for optimizing the source code.
- After GIMPLE, the source code is converted into the static single assignment (SSA) representation.
- The central idea of this form is the fact that each variable is assigned to only once, but can be used at the right hand side of an expression many times.
- The SSA form is also used for optimizations. GCC performs more than 20 different optimizations on SSA trees.
- After the SSA optimization pass, the tree is converted back to the GIMPLE form.
- Convert into another representation called GIMPLE
- Convert into the Static Single Assignment
- Process the SSA optimization passes
- Convert back to the GIMPLE form
Back end
Deal with the target system
- RTL is a hardware-based representation that corresponds to an abstract target architecture with an infinite number of registers.
- An RTL optimization pass optimizes the tree in the RTL form.
- Finally, a GCC back end generates the assembly code for the target architecture using the RTL representation.
- Convert into another representation called GIMPLE
- Process RTL optimization pass
- Generate the assembly code for the target architecture
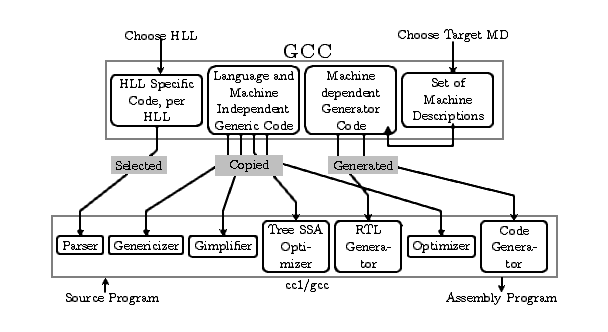
GCC compiler generation framework
Link Time Optimization
- Optimazation is restricted to a translation unit (a single file)
- All files are available only at link time
- LTO enables interprocedural optimization across different files
Optimizing real-world applications with GCC Link Time Optimization
Reference
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compiler
- https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/GNU_C_Compiler_Internals/GNU_C_Compiler_Architecture